無料ダウンロード q table probability 216382-Q table probability
Critical Values of Studentized Range Distribution(q) for Familywise ALPHA = 05 Denominator Number of Groups (aka Treatments) DF 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10This video tutorial provides a basic introduction into conditional probability It explains how to calculate it using sample space It includes example pro2 The probability that medical specialist will remain with a hospital is 06 The probability that an employee earns more than 40,000 per month is 05
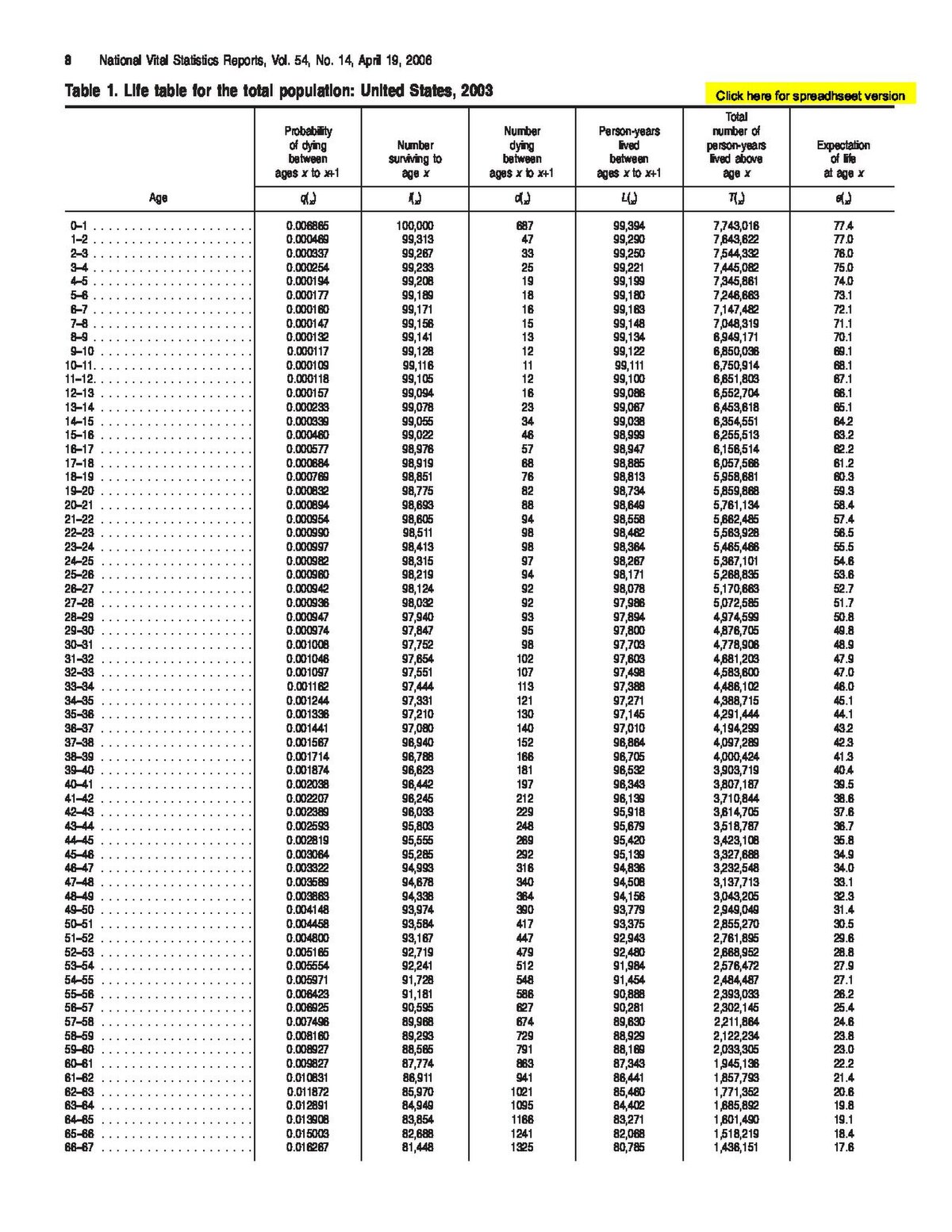
Life Table Wikipedia
Q table probability
Q table probability-Critical values of the studentized range distribution (Q) are commonly used in Tukey's range test A continuous probability distribution that arises during the estimation of the range of a normally distributed population in circumstances where the population SD is unknown and the size of the sample is also less is called as the Studentized range distributionZtable A ztable, also known as a standard normal table or unit normal table, is a table that consists of standardized values that are used to determine the probability that a given statistic is below, above, or between the standard normal distribution The table below is a righttail ztable



Finding The Probability Of A Binomial Distribution Plus Mean Standard Deviation Youtube
We show the probability for each pair in the following table x=length 129 130 131 y=width 15 012 042 006 16 008 028 004 The sum of all the probabilities is 10 The combination with the highest probability is (130;15) The combination with the lowest probability is (131;16) The joint probability mass function is the funcQ Based on the chart, what is the experimental probability of pulling a green marble? When you calculate probability, you're attempting to figure out the likelihood of a specific event happening, given a certain number of attempts Probability is the likliehood that a given event will occur and we can find the probability of an event using the ratio number of favorable outcomes / total number of outcomesCalculating the probability of multiple events is
The PRODUCT of all the integers from 1 to n ex 4!=4x3x2x1=24X Q(x) erfc(x) x Q(x) erfc(x) x Q(x) erfc(x) 3,00 0, 0, 3,50 0, 7,4310E07 4,00 0, 1,5417E08 3,01 0, 0,Set up a table with x, and P(x) x= what you are trying to findP(x)=the probabilities associated with x For a binomial experiment, let p represent the probability of success, and let q represent the probability of failure on a single trial What is a factorial?
Qcrit for df = 1 is 3685 and the Qcrit for df = 240 id 3659 A linear interpolation would give the value , which can be calculated using the Real Statistics formula =QCRIT(4,156,005,2) The Real Statistics formula =QINV(005,4,156,2), which does not use the table, will usually give a more accurate answer, which in this case isSchaum's Outline of Probability and Statistics CHAPTER 2 Random Variables and Probability Distributions 35 EXAMPLE 22 Find the probability function corresponding to the random variable X of Example 21 Assuming that the coin is fair, we have Then The probability function is thus given by Table 22 P(X 0) P(TT) 1 4 P(X 1) P(HTQ() ≈ 10−4 (3) This means p 2E b/N 0 = 3545 Or 2E b/N 0 = Or E b/N 0 = 625 In dB, this is E b/N 0 = 10log 10 625 = 798 dB (4) The more accurate answer is of course 84 dB as shown in the slides You can get a fairly accurate answer if the probability of error was less than 196 × 10−4 For example, what E b/N 0 would you need to have a bit




Probability Of Procedures By Socioeconomic Quintile Q And Hazard Download Table



Http Webspace Ship Edu Pgmarr Geo441 Lectures Lec 5 normality testing Pdf
• Let Pr(X ≤ x) represent "the probability random variable X takes on a value less than or equal to x" This is the cumulative probability of the event DEFINITION The probability mass functi on (pmf) assigns probabilities for all possible outcomes of a discrete random variable EXAMPLE The pmf for X~b(3, 25) is shown in Table 1This relationship is determined by a calibration process using empirical data To estimate a new quality score, the quality predictor values are computed for a new baseQ has an expert system which automatically selects the most appropriate statistics to show on a table Most commonly, these are percentages and averages Alternative statistics can be shown within each cell, to the right of the table or below the table
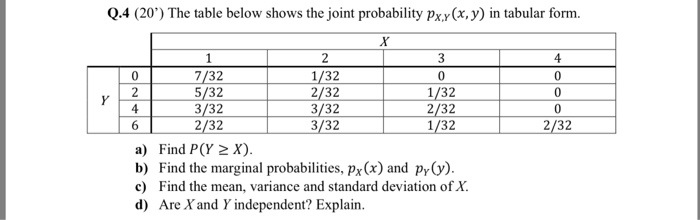



Q 4 The Table Below Shows The Joint Probability Chegg Com




Answered Q 5 Suppose X Is A Discrete Random Bartleby
Q ( x = 1 p 2ˇ Z 1 x e t 2 = 2 dt calculator) Q ( x ) ˇ 1 (1 a ) x a p x 2 b 1 p 2 ˇ e x 2 = 2;Table 4 Binomial Probability Distribution Cn,r p q r n−r This table shows the probability of r successes in n independent trials, each with probability of success pExample of Using a Contingency Table to Determine Probability Step 1 Understanding what the Table is Telling you The following Contingency Table shows the number of Females and Males who each have a given eye colorNote that, for example, the table show that Females have Black eyes and that 10 Males have Gray eyes
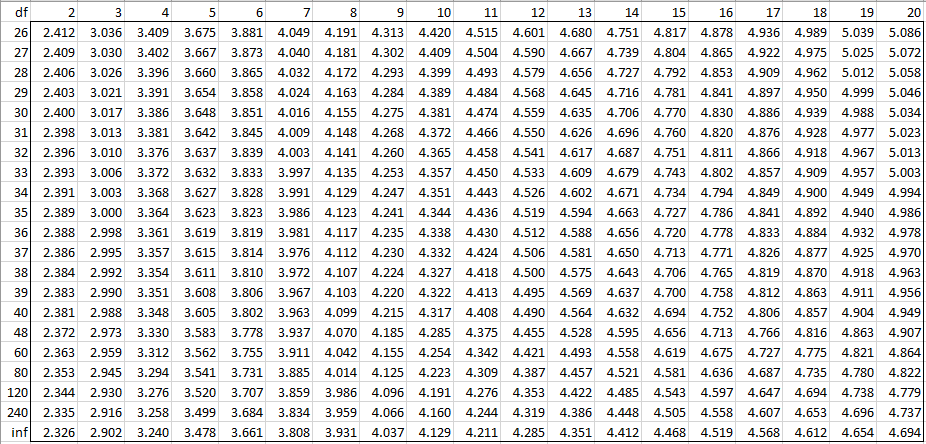



Studentized Range Q Table Real Statistics Using Excel




Solved 51 Q 5 Suppose X Is A Discrete Random Variable Wi Chegg Com
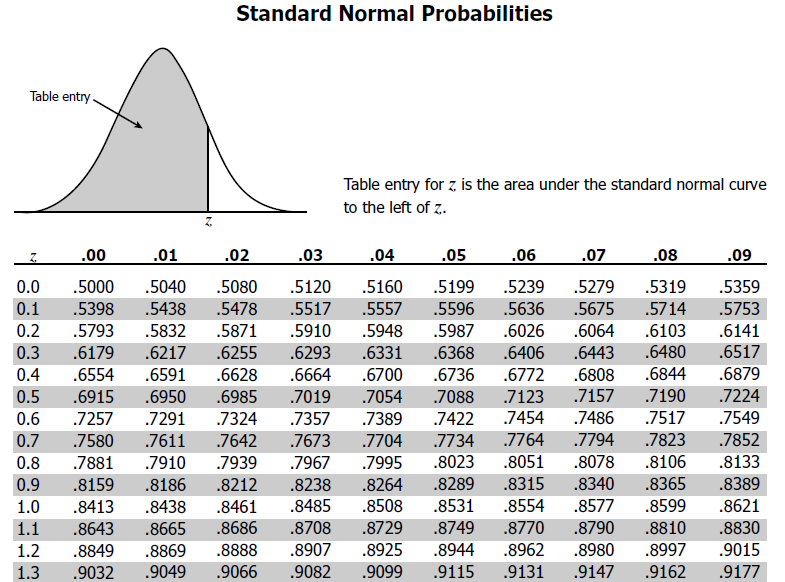
Table H2 Critical Values of Q (p = 001) (p) = 001 k df 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1 900 135 164 186 2 216 227 237 246 2 1390 1902 2256 2537 2776 2986 3173 3341 3493 3 6 1062 1217 1332 1424 1500 1565 1621 1671 4 651 812 917 996 1058 1110 1154 1192 1226 5 570 698 780 842 1 932 967 997 1024In the present work, we use a Gaussian Mixture Model 2 to estimate the probability density function in the joint space of state, action, and q value to approximate the qdistribution of a continuous stateaction RL problemTables • T3 Table entry for z is the area under the standard normal curve to the left of z Probability z TABLE A Standard normal probabilities (continued) z00




Appendix A Tables Business Statistics For Contemporary Decision Making 7th Edition Book




Table 2 From Correlation Of Ventilation Perfusion V Q Scan Results As Compared With Clinical Probability Of Pulmonary Embolism In African American Population Semantic Scholar
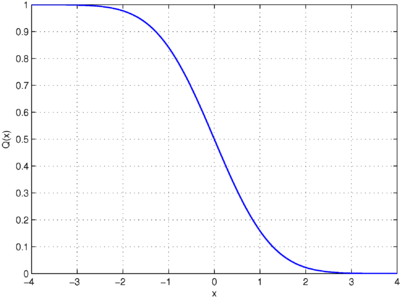
Y = qfunc(x) returns the output of the Q function for each element of the realvalued input The Q function is (1 – f), where f is the result of the cumulative distribution function of the standardized normal random variable For more information, see Algorithms There are $6$ people, let's call them (a,b,c,d,e,f), to sit at a round table The number of ways they can arrange themselves is $(61)!Where a 1 =ˇ , b 2 ˇ Bound Q ( x ) < 1 2 e x 2 = 2 unctions Q ( x = 1 2 erfc x p 2 ;




The Mean And Standard Deviation Of Binomial Probability Distributions




S1esvmc Xgz7vm
Table 4 V/Q Scanning, Pretest Probability for PE*, and Incidence of PE Table 5 Wells' Criteria for Assessment of Pretest Probability for Pulmonary Embolism Scan Report Incidence of PE Overall performance Normal scan2 A quality model, also known as a quality table or Qtable, lists combinations of quality predictor values and relates them to corresponding quality scores;This section will calculate the 05 and 01 critical values for the Studentized range statistic Q To proceed, enter the number of groups in the analysis (k) and the number of degrees of freedom, and then click «Calculate» Note that the value of k must be between 3 and 10, inclusive




Simplified Example Of Q Table Updating Download Scientific Diagram
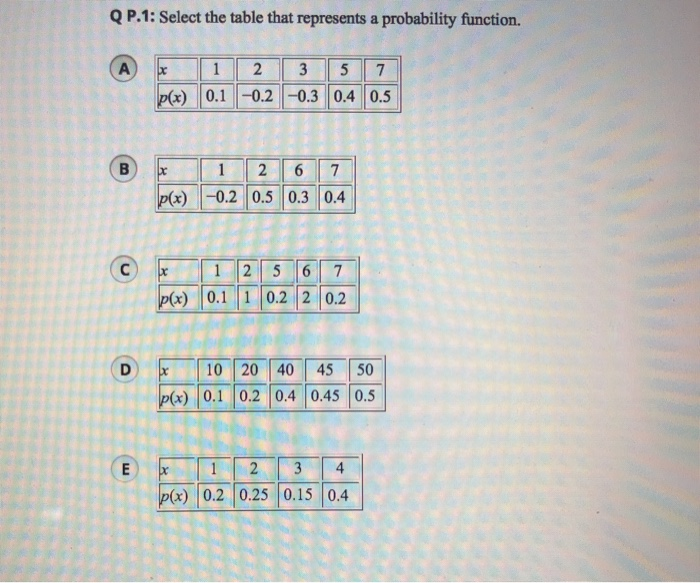



Q P 1 Select The Table That Represents A Probability Chegg Com
Where p is the probability of success q is the probability of failure, where q = 1p Binomial Distribution Vs Normal Distribution The main difference between the binomial distribution and the normal distribution is that binomial distribution is discrete, whereas the normal distribution isSince the normal distribution is symmetrical, only the displacement is important, and a displacement of 0 to 2 or 0 to 2 is the same, and will have the same area under the curve Thus, the probability of a value falling between 0 and 2 is , while a value between 0 and 1 has a probabilityThis video provides an example of how to determine a basic probability from a table expressed as a fraction, decimal, and percentSite http//mathispower4ucom
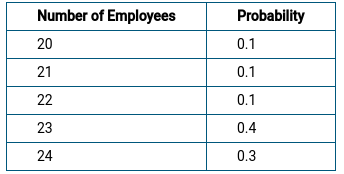



Answered Number Of Employees Probability 0 1 Bartleby
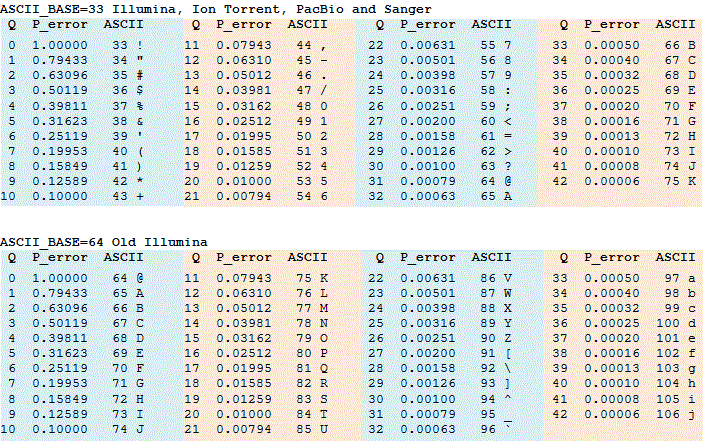



Quality Phred Scores
Normal Distribution Table for ZTest Normaldistribution table & how to use instructions to quickly find the critical (rejection region) value of Z at a stated level of significance (α = 001, 005, 01 etc or α = 01%, 5%, 10% etc) for the test of hypothesis (H 0) in ztest conducted for normally distributed large sample sets in the statistics & probability surveys or experimentsNotice that the 5%, 7%, and 10% defective rates don't go into the table directly This is because they are conditional probabilities and the table is a joint probability table These defective probabilities are conditional upon which company was given That is, the 7% is not P(Defective), but P(DefectiveBrochmailians) Transcribed image text (a) Based on a period life table, the probability that a typical Malaysian will survive the year is An insurance company would like to sell an RM50,000 life term insurance policy If the company wants an expected earning of RM80, determine the annual payment for the insurance policy




Multi Threshold Algorithm Based On Havrda And Charvat Entropy For Edge Detection In Satellite Grayscale Images




Find The Following Probability Q Function Of Chegg Com
Table of Qfunction values To find Q(1365) look under column x to find 135 Then proceed on this row till you come to the column under 0015 Read off the value as 8613 x 102 x 0000 0005 001 0015 002 0025 0 03 0035 004 0045= 1$ ways What is the probability that person 'a' will have person 'b' sat to his immediate left, and person 'c' sat to his immediate right?TABLE B5 The studentized range statistic (q)* *The critical values for q corresponding to alpha = 05 (top) and alpha =01 (bottom)




5 Anova Performed On The P Q P Data From The Probability Judgment Task Download Table
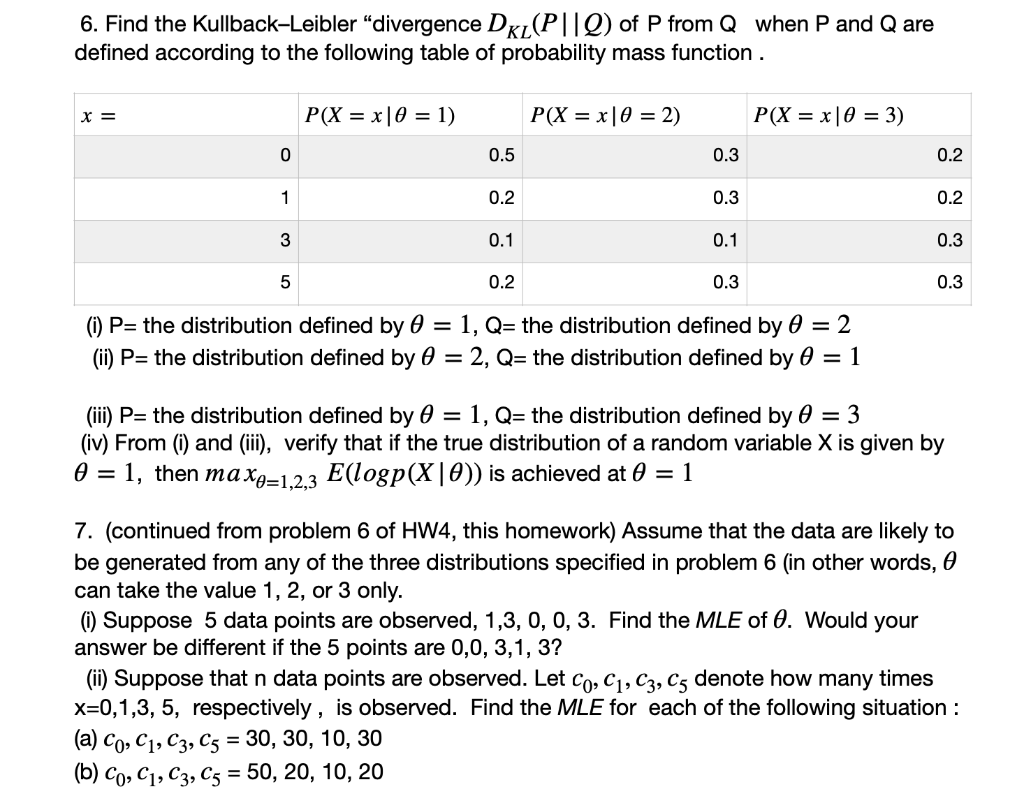



Solved 6 Find The Kullback Leibler Divergence Dkl P Q Chegg Com
Hash Table Probability that the longest chain has length k Say I have a hash table of size m, with collision handled by chaining Assume the hash function hashes uniformly, so every key has probability of 1 m of being hashed to any slot in the table I insert n keys into the tablePredicted Q Scores Illumina sequencing Q scores are highly accurate This example shows that predicted Q scores for a HiSeq 00 run correlate well to empirically derived Q scores Empirical quality scores Predicted quality scores 5 10 15 25 30 35 40 5 10 15 25 30 35 40 Table 2 MiSeq vs HiSeq 00 Ecoli K12 MG1655 Data Comparison The probability that the team scores exactly 2 goals is 035 And so on Properties of a Probability Distribution Table A probability distribution table has the following properties 1 All probabilities must add up to 1 For a probability distribution table to be valid, all of the individual probabilities must add up to 1



1
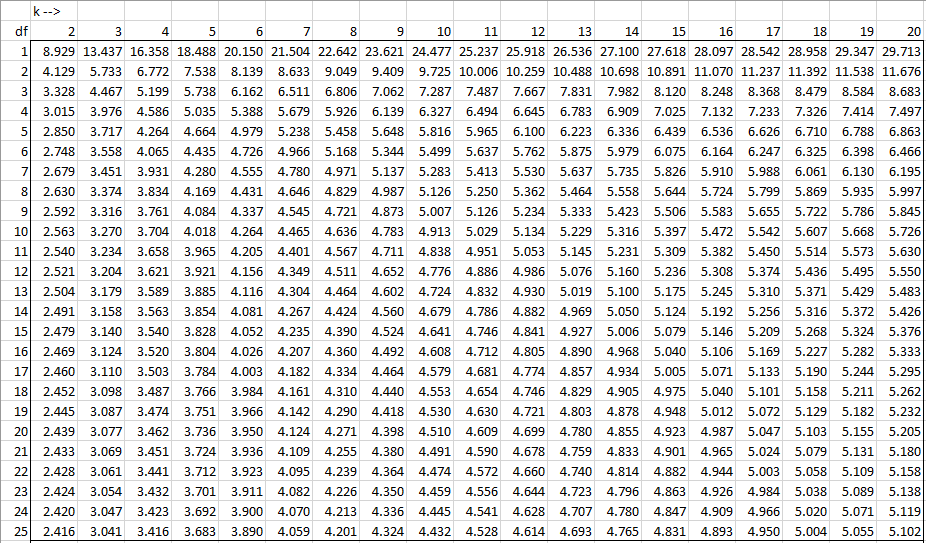



Studentized Range Q Table Real Statistics Using Excel
Normal distribution table When we are finding the probability, it is important to note whether we are looking for the probability to the left, right, or between variables If we are looking to the left (or less than the random variable), we find the probability in the table and leave it alone If we areThe probability of getting exactly x success in n trials, with the probability of success on a single trial being p is P(X=x) = nCx * p^x * q^(nx) Example A coin is tossed 10 times What is the probability that exactly 6 heads will occur Success = "A head is flipped on a single coin" p = 05;I'm confused on how to go about this



Link Springer Com Content Pdf m 3a978 3 319 8 2f1 Pdf
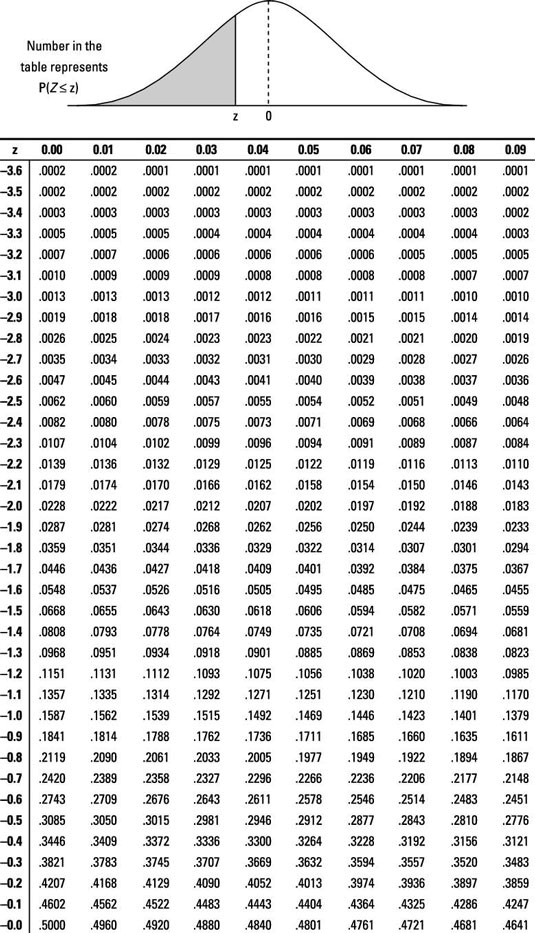



Jzdawshd2jzvgm
The normal probability table always lists percentiles To find the area to the right, calculate 1 minus the area to the left For additional details about working with the normal distribution and the normal probability table, see Section 41 ∗ ∗ For Z≤−350, Z ≤ − 350, the probability is less than or equal to Answered 3/46 First find the probability of picking a red crayon (6/24 or 1/4), then find the probability that the second crayon is green (6/23) Multiply the probabilities together to get 3/46 reduced 1 AnswerE&CE 411, Spring 09, Table of Q Function 1 Table 1 Values of Q(x) for 0 ≤ x ≤ 9 x Q(x) x Q(x) x Q(x) x Q(x) 000 05 230 455 263×10−6 680 5231×10−12 005 235 460 ×10−6 685 ×10−12 010 240 465 ×10−6 690 ×10−12 015 245 470 ×10−6 695 164×10−12



1



Link Springer Com Content Pdf m 3a978 3 319 8 2f1 Pdf
The qGaussian is a probability distribution arising from the maximization of the Tsallis entropy under appropriate constraints It is one example of a Tsallis distribution The qGaussian is a generalization of the Gaussian in the same way that Tsallis entropy is a generalization of standard Boltzmann–Gibbs entropy or Shannon entropy The normal distribution is recovered as q → 1 The qGaussian The probability X failing during one year is 025 and that of Y is 005 and that of Z failing is 015 what is the probability that the equipment will fail before the end of one year?Q You flip a nickel three times Find the probability that all flips will land on tails Q Suppose you pay $100 to roll a fair die with the understanding you will get $300 back rolling a 4 or a 2, and nothing otherwise What is the expected amount you win?



Link Springer Com Content Pdf m 3a978 3 319 8 2f1 Pdf
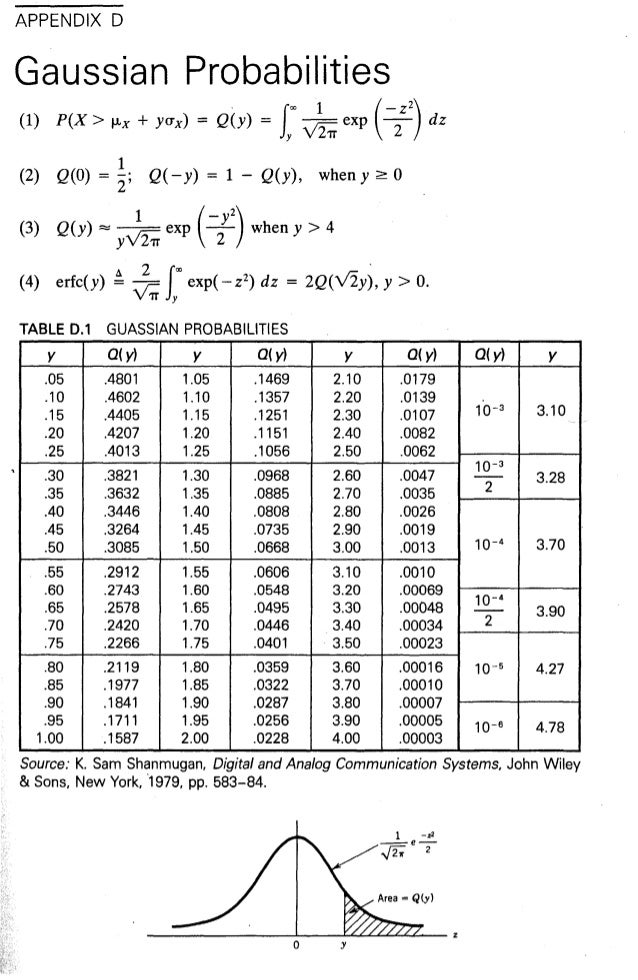



Table Gaussian
math statistics and probability statistics and probability questions and answers Q P1 Select The Table That Represents A Probability Function B 1 2 3 5 7 P (x) 01 02 03 Question Q P1 Select The Table That Represents A Probability FunctionErfc( x 2 Q ( x p 2) y Q ( x 1 Q ( x ) x 009 000 e01 010 e01 0 e01 030 347e01 040 317e01 050 e01 060 e01 070 e01 080 e01 090 e01




2 The Marginal Probability P Rpy 2 1q And The Conditional Probability Download Table




1 Down Probability As A Function Of Node Failure Probability Q Q P Download Table




Z Score Table Formula Distribution Table Chart Example



How To Find A Percentile For A Normal Distribution Dummies



3




Chapter 13 Book And Slides Examples Flashcards Quizlet



Link Springer Com Content Pdf m 3a978 3 319 8 2f1 Pdf
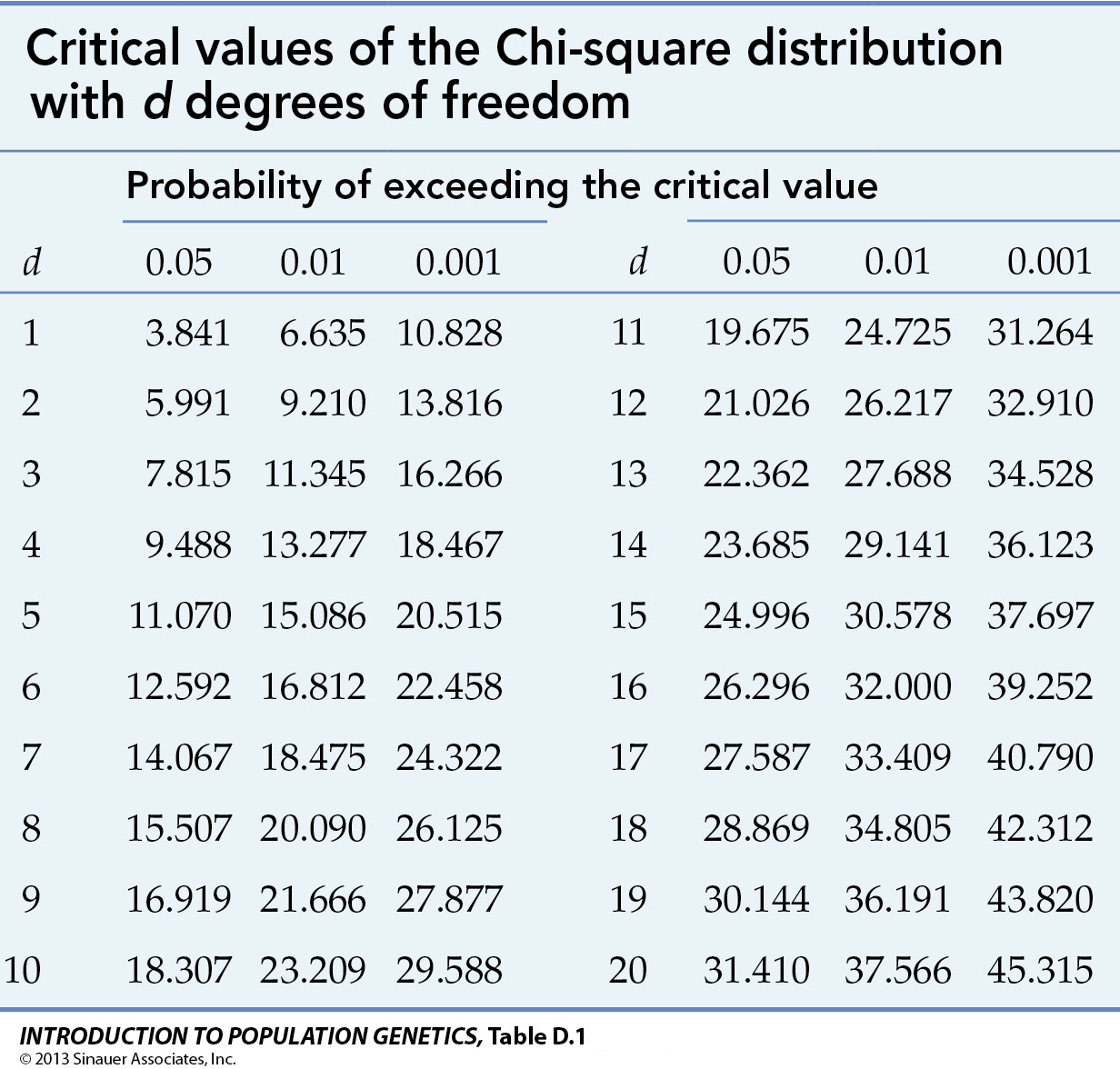



Ns Table D Chi Square
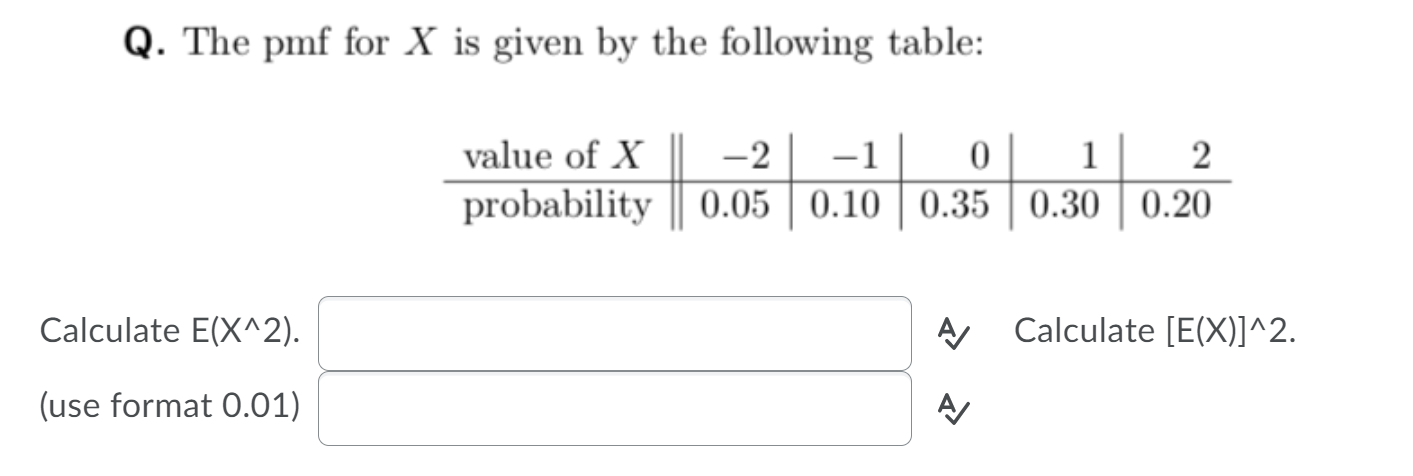



Solved Q The Pmf For X Is Given By The Following Table Chegg Com




Scielo Brasil A Simplified Approach For Reliability Evaluation And Component Allocation In Three State Series And Parallel Systems Composed Of Non Identical Components A Simplified Approach For Reliability Evaluation And Component Allocation




Critical Values For The Skewness Test 95 Confidence Limit And The Download Table



Www2 Chemistry Msu Edu Courses Cem434 Lecture Statistics Total Pdf




Class 9 Ch 15 Q 46 Q 47 Probability Support Material Important Questions Cbse Ncert Youtube
/dotdash_Final_Probability_Distribution_Sep_2020-01-7aca39a5b71148608a0f45691b58184a.jpg)



Probability Distribution Definition
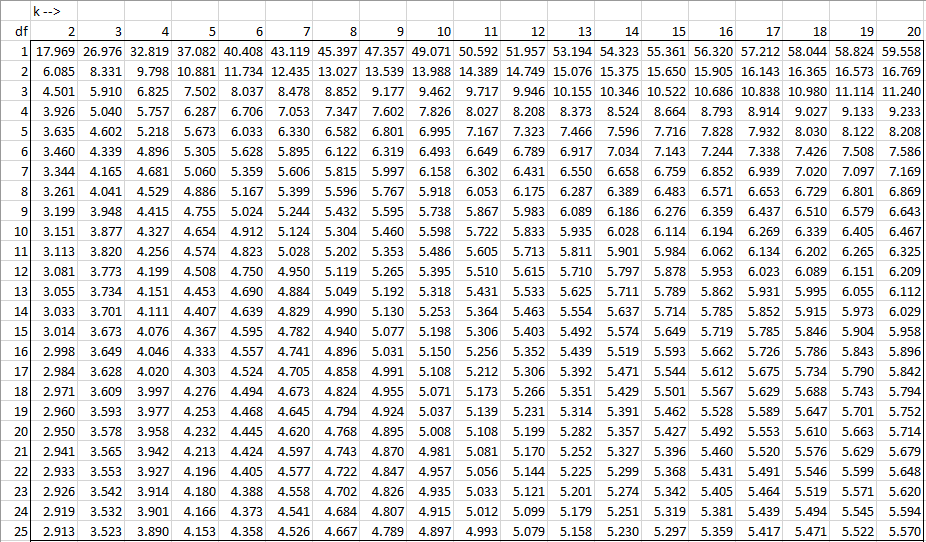



Studentized Range Q Table Real Statistics Using Excel




Solving Problem By Given Expected Value And Standard Daviation With Tables Mathematics Stack Exchange




Ljung Box Q Statistics And Corresponding P Value Download Table



Link Springer Com Content Pdf m 3a978 3 319 8 2f1 Pdf
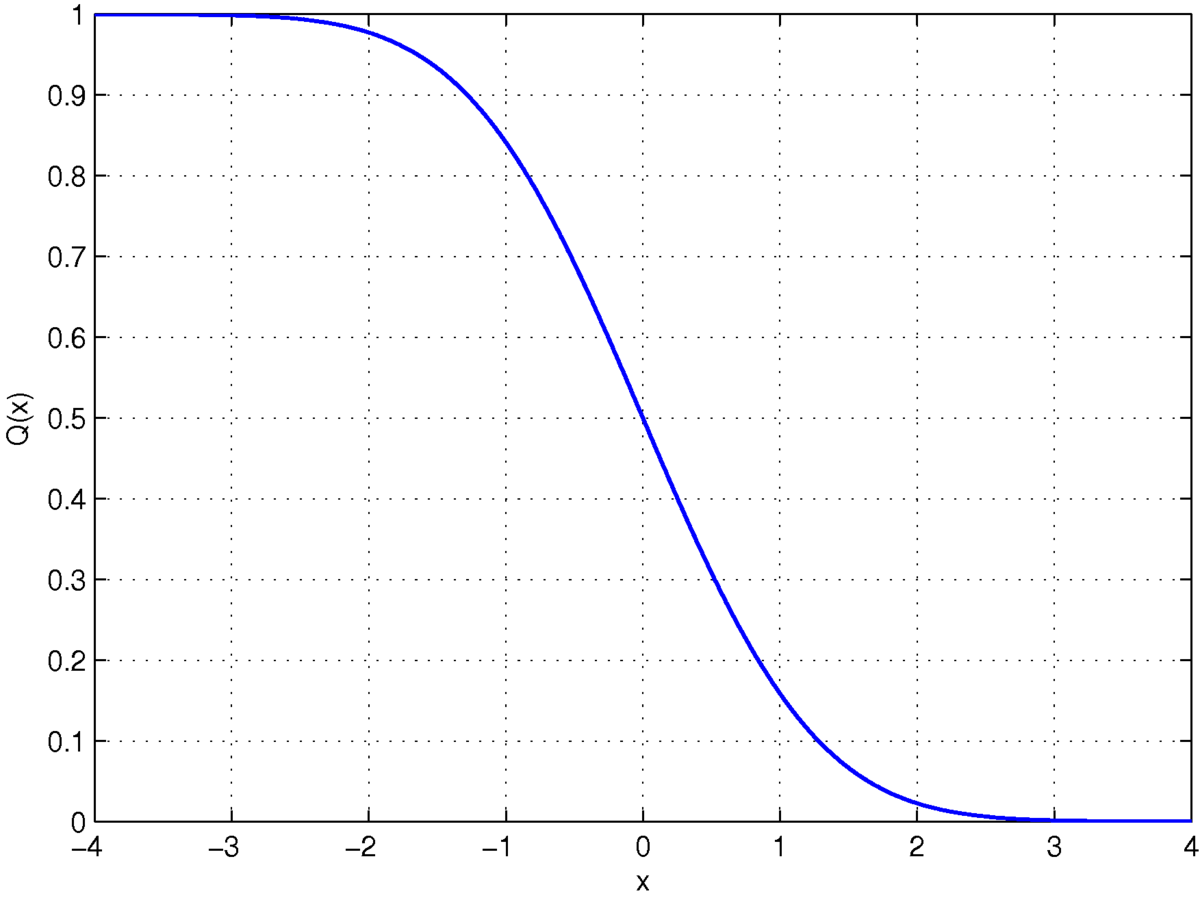



Q Function Wikipedia




The Probability Density Function Pdf F Q G For Chegg Com




Using Contingency Tables To Calculate Probabilities Statistics By Jim
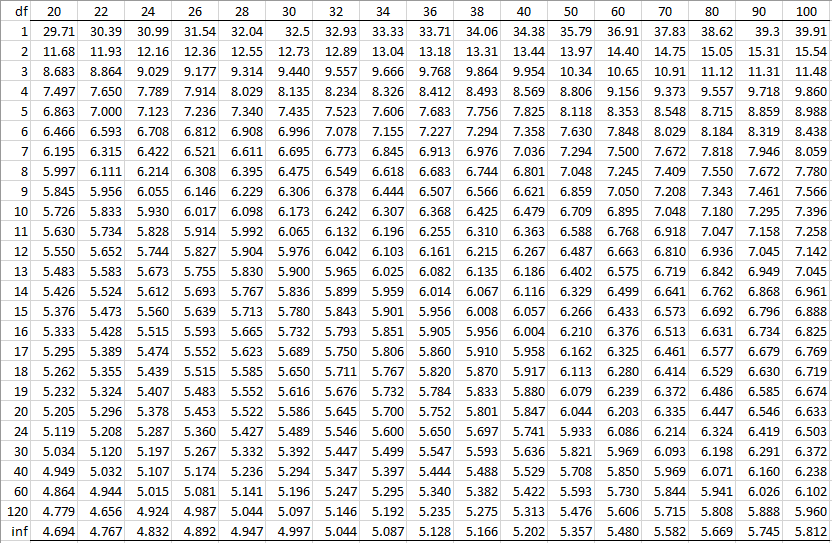



Studentized Range Q Table Real Statistics Using Excel




Using Contingency Tables To Calculate Probabilities Statistics By Jim




Finding The Probability Of A Binomial Distribution Plus Mean Standard Deviation Youtube




Table 1 From Correlation Of Ventilation Perfusion V Q Scan Results As Compared With Clinical Probability Of Pulmonary Embolism In African American Population Semantic Scholar
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_The_Normal_Distribution_Table_Explained_Jan_2020-06-d406188cb5f0449baae9a39af9627fd2.jpg)



The Normal Distribution Table Definition




Life Table Wikipedia



Link Springer Com Content Pdf m 3a978 3 319 8 2f1 Pdf



Http Webspace Ship Edu Pgmarr Geo441 Lectures Lec 5 normality testing Pdf




Manager Ii S Winning Probability Q N Download Table



Q Function Wikipedia
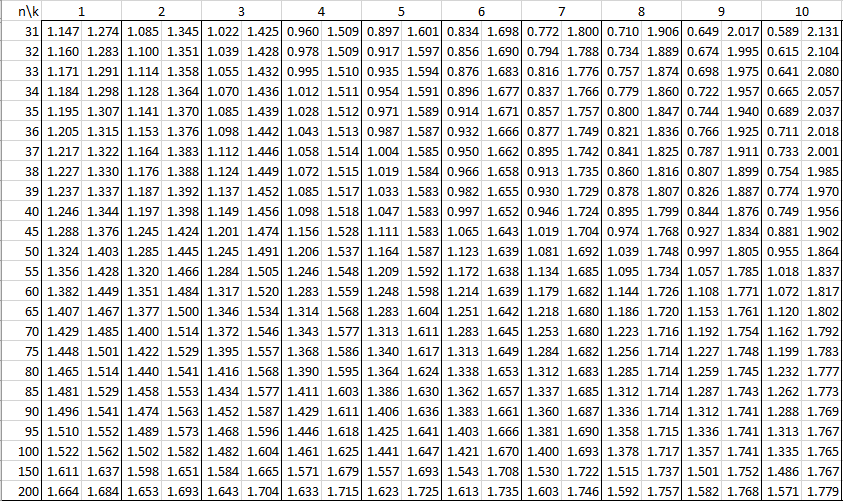



Durbin Watson Table Real Statistics Using Excel




Values Of Marginal Probability P F N And Of The Function Q N L In La Download Table
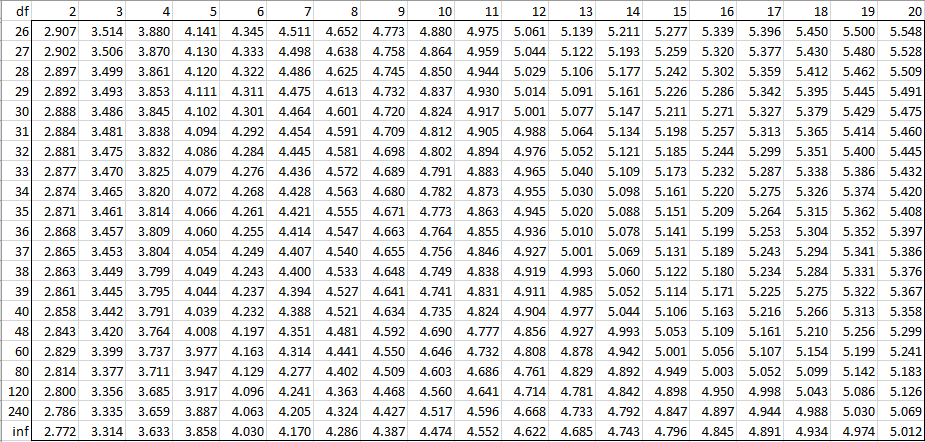



Studentized Range Q Table Real Statistics Using Excel
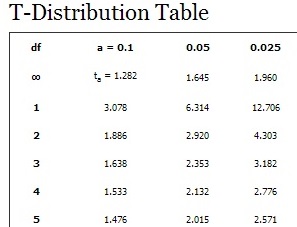



Degrees Of Freedom What Are They Statistics How To




Q Function Wikipedia




An Introduction To Q Learning Reinforcement Learning




Table 1 From Analysis Of Hashrate Based Double Spending Semantic Scholar



Onlinelibrary Wiley Com Doi Pdf 10 1002 App3




Q 1 Z Is The Standard Normal Variable Use Table 1 Chegg Com




Probability Mass Function Youtube




Levy Distribution Chart Calculator High Accuracy Calculation




The Runoff Peak P Q Order Number In M Probability Of Exeedence P Download Table



1




Q Function Wikipedia




Z Score Table Formula Distribution Table Chart Example




Q Learning Wikipedia




Nqm A Priori Probabilities P Sn Q Download Table
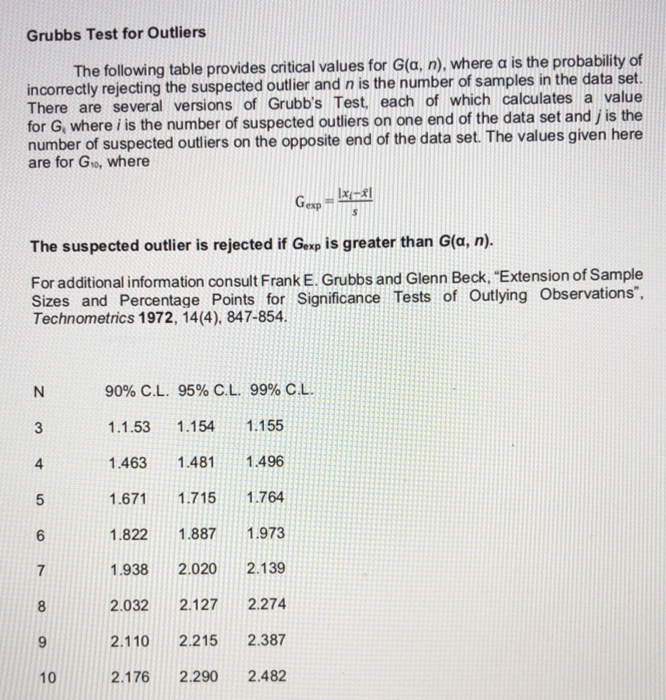



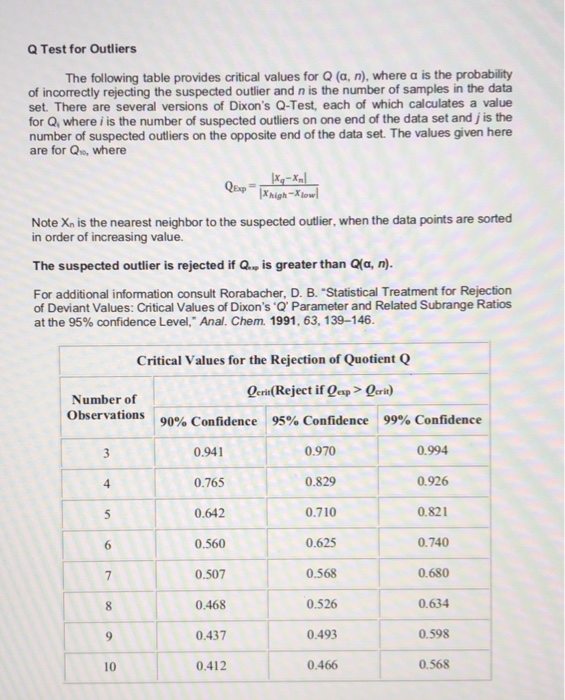
Q Test For Outliers The Following Table Provides Chegg Com



Plos One Development And Psychometric Validation Of The Ede Qs A 12 Item Short Form Of The Eating Disorder Examination Questionnaire Ede Q




Diagonestic Tests Q Statistic Probabilities Adjusted For 4 Dynamic Download Table




Wilcoxon Signed Ranks Table Real Statistics Using Excel




Probability Of Procedures By Socioeconomic Quintile Q And Hazard Download Table



Casd
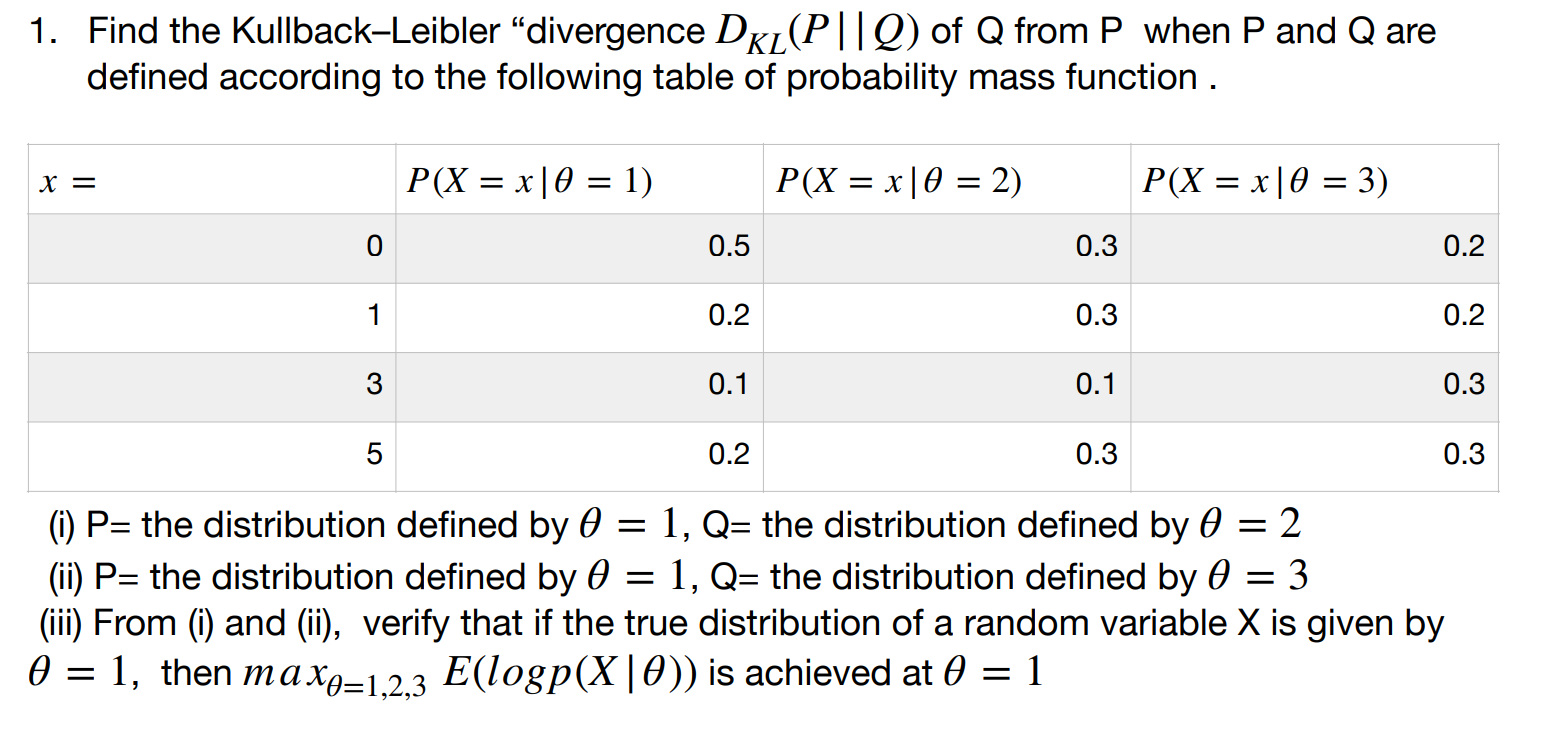



Solved 1 Find The Kullback Leibler Divergence Dr1 P Q Chegg Com



Solved 10 Assume Random Variable X Follows A Probability Distribution Shown In The Table Below Determine The Mean And Standard Deviation Of X Sh Course Hero
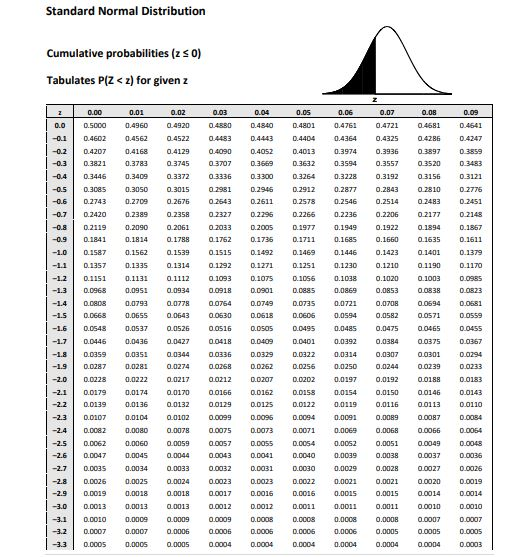



Q 1 Suppose X Is A Binomial Random Variable With N Chegg Com
/JointProbabilityDefinition2-fb8b207be3164845b0d8706fe9c73b01.png)



Joint Probability Definition
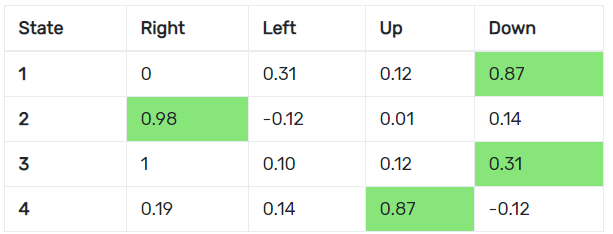



How To Teach Ai To Play Games Deep Reinforcement Learning By Mauro Comi Towards Data Science




Table 1 From Divergence From And Convergence To Uniformity Of Probability Density Quantiles Semantic Scholar




4th Quarter 09 E Commerce Table 3
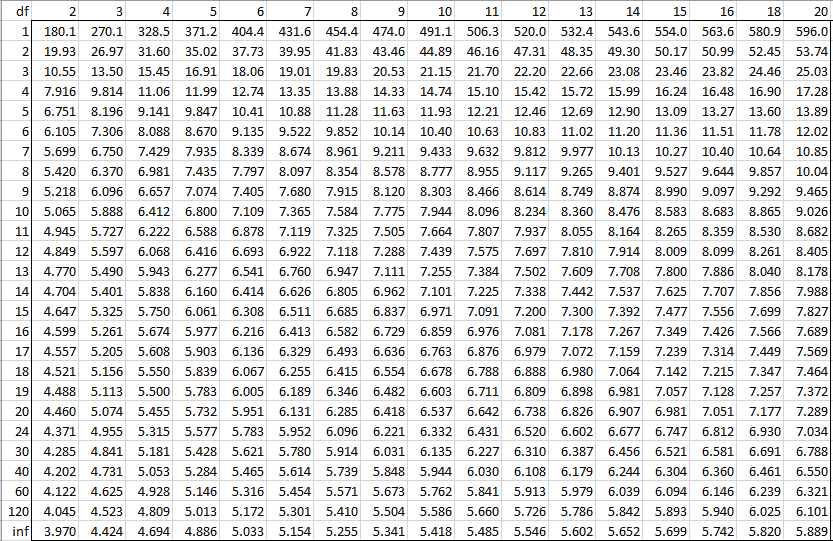



Studentized Range Q Table Real Statistics Using Excel
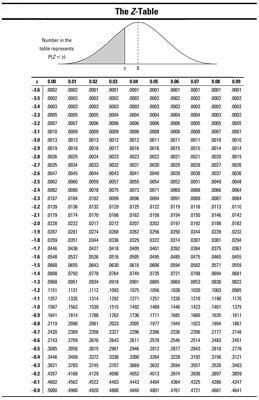



How To Find A Percentile For A Normal Distribution Dummies




2 3 Mean Comparisons



8 Q Table Statistics Pdf




Table 4 From Correlation Of Ventilation Perfusion V Q Scan Results As Compared With Clinical Probability Of Pulmonary Embolism In African American Population Semantic Scholar
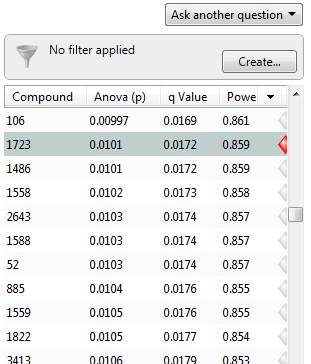



What Are P Values What Are Q Values And Why Are They Important



Q Test For Outliers The Following Table Provides Chegg Com



Link Springer Com Content Pdf m 3a978 3 319 8 2f1 Pdf
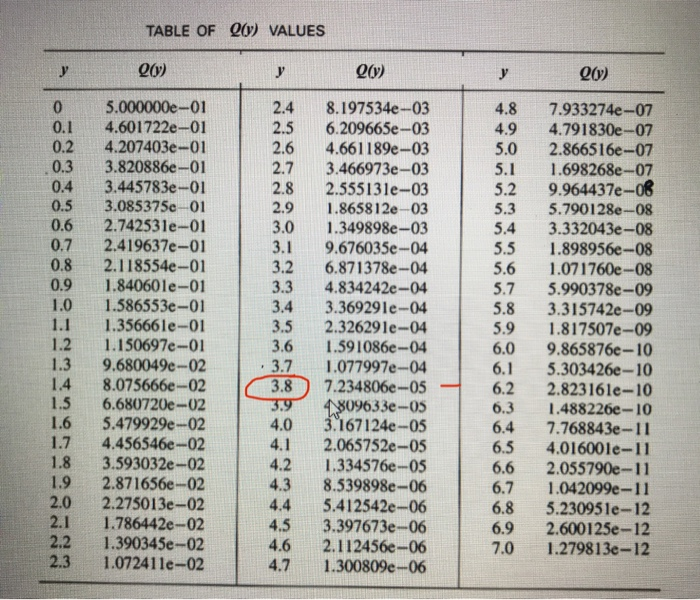



My Last Student Number Is 8 In The Table Chegg Com
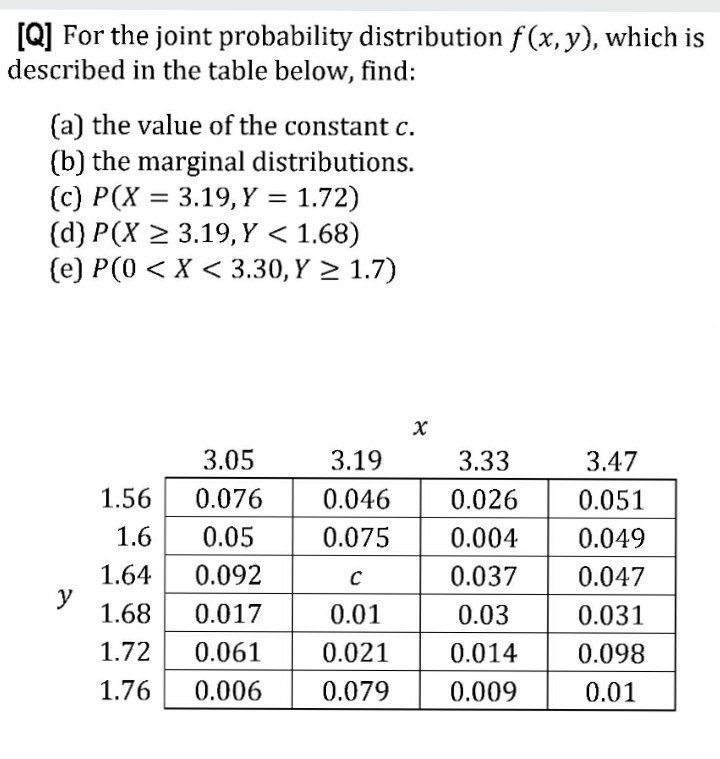



Answered Q For The Joint Probability Bartleby




Practical Reinforcement Learning 02 Getting Started With Q Learning By Shreyas Gite Towards Data Science




Probability Of Having At Least One Dummy For 3 Players In Download Table
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_The_Normal_Distribution_Table_Explained_Jan_2020-01-091f853d86c444f3bd7cd32c68fc0329.jpg)



The Normal Distribution Table Definition




5 2b Standard Normal Distribution Tables Example 1 Spm Additional Mathematics




The Probability Of Success For All Settings N M Q As Approximated Download Table
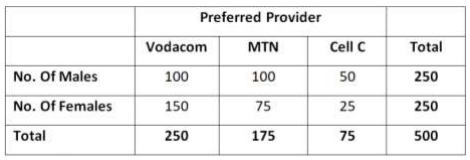



As A Quantitative Techniques Student You Are Required



Z Score Table Formula Distribution Table Chart Example


コメント
コメントを投稿